Healthcare Robotics Investment: Boost Efficiency & Cut Errors in US Hospitals
Investing in healthcare robotics directly improves operational efficiency and significantly reduces medical errors in US hospitals by automating tasks, assisting clinical staff, and enhancing patient care through precision and data-driven insights.
In the dynamic landscape of modern healthcare, the pursuit of efficiency and error reduction is relentless. Investing in Healthcare Robotics: A Guide to Improving Efficiency and Reducing Errors in US Hospitals is no longer a futuristic concept but a strategic imperative. This guide delves into how leveraging advanced robotics can transform hospital operations, ensuring patient safety and optimizing resource utilization across the United States.
The Dawn of Robotic Healthcare: A New Era of Precision
The integration of robotics into healthcare represents a significant paradigm shift, moving from traditional manual processes to highly automated and precise interventions. This evolution promises not only to streamline complex procedures but also to elevate the standard of patient care. The advent of robotics in hospitals, particularly in the US, is driven by the pressing need to address persistent challenges such as rising operational costs, aging populations, and the ever-present demand for higher quality care with fewer errors.
Robotic systems are multifaceted, encompassing everything from surgical assistants to autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) for logistics. Their applications extend beyond the operating theater into pharmacies, laboratories, and even patient rehabilitation. This broad utility underscores the potential for a comprehensive transformation of healthcare delivery, allowing human professionals to focus on tasks that truly require their unique cognitive and empathetic skills.
Types of Robotics Transforming US Hospitals
The spectrum of robotic applications in healthcare is vast and continually expanding. Understanding the distinct categories and their specific functions is crucial for strategic investment and implementation. These technologies are designed to augment human capabilities, not replace them entirely, by handling repetitive, high-precision, or high-risk tasks.
- Surgical Robots: Enhance precision, dexterity, and control for surgeons, leading to minimally invasive procedures and faster patient recovery times.
- Pharmacy Automation: Automate dispensing, compounding, and inventory management of medications, drastically reducing dispensing errors and improving efficiency.
- Logistics Robots (AMRs): Transport supplies, pharmaceuticals, and waste within hospitals, optimizing workflow and reducing staff workload.
- Rehabilitation Robots: Assist patients in regaining motor functions, providing consistent, data-driven therapy that is often more intensive than traditional methods.
Additionally, disinfection robots are gaining prominence, especially in the wake of global health crises. These robots utilize UV light or other advanced mechanisms to sanitize patient rooms and operating theaters, contributing to infection control and enhancing overall hospital hygiene. The collective impact of these diverse robotic applications is a more robust, efficient, and safer healthcare environment.
In essence, robotic healthcare is still in its nascent stages, yet its trajectory is steep. Early adopters are already witnessing substantial benefits, setting a precedent for wider integration. The strategic deployment of these technologies requires careful planning, robust infrastructure, and a clear understanding of both the immediate and long-term returns on investment.
Boosting Operational Efficiency with Robotics
Operational efficiency is the bedrock of a thriving healthcare system, allowing hospitals to deliver high-quality care while managing resources effectively. Robotics plays a pivotal role in optimizing various aspects of hospital operations, from the mundane to the highly complex. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, robots free up highly skilled human staff to focus on direct patient interaction and critical decision-making, where their expertise is most valuable.
Consider the daily routines within a large hospital: countless items need to be moved, medications dispensed, and patient records managed. These tasks, while essential, consume significant staff time that could otherwise be dedicated to patient care. Robotic solutions provide an untiring, consistent, and error-free alternative. This not only enhances productivity but also improves staff morale by alleviating the burden of physically demanding or monotonous duties.
Streamlining Workflow and Resource Allocation
Robots can operate 24/7, tirelessly performing tasks that require consistency and precision. This continuous operation significantly reduces bottlenecks and accelerates various hospital processes. For instance, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) efficiently transport lab samples, medical supplies, and even meals, navigating complex hospital layouts with minimal human intervention. This ensures that necessary resources are available exactly when and where they are needed, reducing delays and improving responsiveness.
- Automated Supply Delivery: AMRs ensure timely delivery of medical supplies, reducing manual labor and stockouts.
- Optimized Lab Sample Transport: Robots quickly move samples between departments, speeding up diagnostic processes.
- Efficient Waste Management: Robotic systems assist in the disposal of medical waste, improving hygiene and safety.
Furthermore, the data generated by these robotic systems provides invaluable insights into operational bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Hospitals can analyze robot pathways, delivery times, and task completion rates to further refine their layouts and staffing strategies. This data-driven approach to efficiency management is a significant advantage over traditional, less quantifiable methods.
Beyond logistics, robotic process automation (RPA) can streamline administrative tasks, such as managing patient appointments, processing insurance claims, and updating electronic health records (EHRs). While not physical robots, RPA software bots significantly reduce the time and error rate associated with these data-intensive processes, contributing to overall operational fluidity and enabling faster patient access to care.
The fundamental goal of integrating robotics for efficiency is to create a leaner, more agile hospital environment that is better equipped to handle the growing demands of modern healthcare. By systematically leveraging these technologies, hospitals can achieve substantial operational gains, translating into better patient outcomes and improved financial health.
Reducing Medical Errors: A New Frontier in Patient Safety
Medical errors remain a critical concern in healthcare, often leading to adverse patient outcomes, increased healthcare costs, and diminished public trust. Robotics offers a powerful solution by introducing unparalleled precision, consistency, and data validation into clinical processes. By minimizing the human element in error-prone tasks, robots significantly enhance patient safety across various hospital departments.
Think about medication dispensing, surgical procedures, or even diagnostic readings. Each of these steps carries a risk of human error, no matter how skilled and diligent the medical professional. Robotic systems, however, are programmed to follow exact protocols, reducing variability and eliminating fatigue-related mistakes. This inherent reliability makes them invaluable tools in mitigating some of the most common causes of medical errors.
Precision in Surgery and Medication Management
Surgical robots, such as the da Vinci system, offer surgeons enhanced dexterity, magnified 3D vision, and tremor reduction. This allows for minimally invasive procedures with greater precision, leading to smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, faster recovery times, and ultimately, fewer complications. The robot acts as an extension of the surgeon’s hands, enabling intricate maneuvers that might be challenging or impossible with traditional methods.
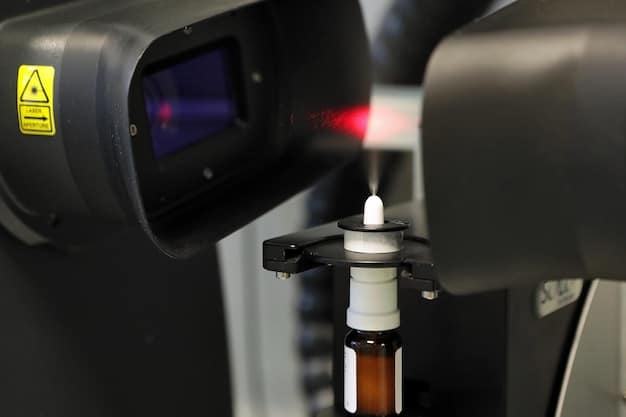

Similarly, in pharmacies, robotic dispensing systems eliminate the risk of human transcription errors, miscounts, or incorrect medication selection. These systems can verify prescriptions against patient records, check for drug interactions, and accurately dispense doses. This level of automated verification acts as a crucial safety net, protecting patients from medication-related harm.
- Reduced Surgical Complications: Robotic assistance minimizes invasiveness, leading to fewer post-operative issues.
- Elimination of Dispensing Errors: Automated systems ensure correct medication, dosage, and patient matching.
- Improved Dosage Accuracy: Robots can measure and compound medications with extreme precision, reducing under- or overdosing risks.
Beyond these direct applications, robotics also contributes to error reduction through improved data management and analytics. Robots can collect vast amounts of data on their performance, which can then be analyzed to identify patterns of potential risk or inefficiency. This predictive capability allows hospitals to proactively address issues before they lead to errors, fostering a culture of continuous improvement in patient safety.
The ultimate benefit of integrating robotics for error reduction is the profound impact on patient well-being. A reduction in medical errors means fewer hospital readmissions, shorter recovery periods, and a higher quality of life for patients. For hospitals, this translates into enhanced reputation, reduced liability, and a more sustainable healthcare delivery model.
Navigating the Investment Landscape: Costs and ROI
While the benefits of healthcare robotics are compelling, the initial investment can be substantial, prompting careful consideration of costs versus return on investment (ROI). Hospitals must approach these investments strategically, understanding that the long-term gains often far outweigh the upfront expenditures. The financial landscape of robotic integration is complex, involving not just purchase costs but also implementation, maintenance, and training expenses.
It’s crucial to look beyond the sticker price and consider the total cost of ownership over the lifetime of the robotic system. This includes recurring costs like software updates, parts replacement, and specialized technical support. However, these costs are typically offset by significant operational savings and improved patient outcomes.
Understanding the Financial Implications
The acquisition cost of a single surgical robot can range from $1 million to $2.5 million, with additional costs for instruments, maintenance contracts, and specialized training for medical staff. Similarly, sophisticated pharmacy automation systems can also represent a significant investment. For logistics robots, while individual units might be less expensive, deploying a fleet across a large hospital can still involve substantial capital outlay.
- Purchase Price: Varies significantly by type and complexity of the robot.
- Installation and Integration: Costs associated with setting up the robotic infrastructure.
- Maintenance and Service Contracts: Ongoing expenses for upkeep and technical support.
- Training and Education: Crucial for staff proficiency and safety.
However, the ROI stems from multiple avenues. Savings are realized through:
- Increased Efficiency: Reduced labor costs, optimized workflows, and faster turnaround times.
- Error Reduction: Fewer adverse events, leading to lower liability costs and improved patient satisfaction.
- Enhanced Capacity: Ability to perform more procedures or handle higher patient volumes.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Faster recovery, shorter hospital stays, and reduced readmissions, which can impact reimbursement models.

Furthermore, some robotic investments can also attract new patients, particularly for specialized robotic surgeries, which can be a key differentiator in a competitive healthcare market. Insurance reimbursements for robotic procedures are also evolving, making these investments more financially viable over time.
The key to maximizing ROI lies in comprehensive planning and a phased implementation strategy. Hospitals should conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses, pilot programs, and continuous performance monitoring to ensure that robotic investments align with their strategic goals and yield tangible financial and clinical benefits. A long-term vision is essential, as the full benefits of robotic integration often unfold gradually over several years.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementation
While the benefits of healthcare robotics are clear, successful implementation is not without its challenges. Hospitals considering this transformative step must anticipate and address various hurdles, ranging from initial resistance and integration complexities to ethical considerations and the need for continuous adaptation. Planning and foresight are paramount to overcoming these obstacles and harnessing the full potential of robotic systems.
One of the primary challenges is securing buy-in from all stakeholders, including clinicians, administrative staff, and IT departments. Resistance often stems from concerns about job displacement, the learning curve associated with new technologies, or the perceived disruption to established workflows. Effective communication and comprehensive training programs are crucial for mitigating these concerns and fostering a collaborative environment.
Addressing Integration and Ethical Concerns
Integrating complex robotic systems into existing hospital infrastructure presents significant technical challenges. Compatibility with current IT systems, electronic health records (EHRs), and other medical devices is essential. Interoperability issues can lead to delays, increased costs, and compromised data flow. Hospitals need robust IT planning and potentially significant upgrades to their digital infrastructure to ensure seamless integration.
- System Compatibility: Ensuring new robots integrate with existing IT and medical equipment.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive patient data handled by robotic systems.
- Workflow Disruption: Managing the transition to new, automated processes.
Ethical considerations also come to the fore. Questions around accountability in the event of a robotic malfunction, the role of human judgment versus machine autonomy, and patient privacy in data-driven systems require careful deliberation. Hospitals must establish clear guidelines and protocols for ethical deployment and ongoing use of robotics, ensuring patient safety and trust remain paramount.
Maintaining and servicing robotic systems is another critical consideration. These are sophisticated machines that require specialized technical support and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Hospitals need to factor in long-term service contracts and potentially train in-house technical staff to handle routine issues, reducing reliance on external vendors.
Finally, the rapid pace of technological advancement means that robotic systems can quickly become outdated. Hospitals need a strategy for future upgrades and replacements, ensuring their investments remain cutting-edge and continue to deliver value. This requires a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation within the organization.
By proactively addressing these challenges, hospitals can lay a strong foundation for successful robotic integration, paving the way for a more efficient, safer, and technologically advanced healthcare system that benefits both providers and patients.
The Future of Robotics in US Healthcare
The journey of robotics in US healthcare is far from over; in fact, it is just beginning to accelerate. As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, the capabilities of robots in hospitals are expected to expand dramatically, leading to even greater levels of efficiency, precision, and personalized care. The future promises a healthcare system where human and artificial intelligence collaborate seamlessly to deliver optimal health outcomes.
One of the most exciting prospects is the development of increasingly intelligent and autonomous robots. Powered by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), future generations of robots will be able to perform more complex tasks, adapt to changing conditions, and even learn from their experiences. This will lead to more sophisticated surgical procedures, predictive diagnostics, and highly personalized treatment plans.
Evolving Applications and Collaborative Technologies
Expect to see a broader adoption of micro-robots for targeted drug delivery and minimally invasive diagnostics, navigating the human body to treat diseases with unparalleled precision. Exoskeletons and advanced prosthetic limbs will become more common, offering revolutionary mobility and rehabilitation solutions for patients with disabilities. Furthermore, companion robots could play a role in elderly care, providing social interaction and monitoring vital signs, alleviating some of the burden on human caregivers.
- Micro-Robots: Precision drug delivery and diagnostics inside the human body.
- AI-Powered Diagnostics: Robots assisting in faster, more accurate disease identification.
- Advanced Prosthetics: More natural and functional robotic limbs.
- Remote Robotic Care: Enabling specialists to perform procedures from a distance.
The concept of IoMT (Internet of Medical Things), where medical devices, sensors, and robots are interconnected, will become mainstream. This will create a vast network of real-time data, allowing for predictive maintenance of equipment, proactive patient monitoring, and highly efficient resource allocation across hospital networks. Such interconnectedness will enhance communication and collaboration between robotic systems and human staff, fostering a truly intelligent hospital environment.
Telemedicine, already boosted by recent global events, will further integrate robotic capabilities. Remote-controlled robots could allow surgeons to perform operations on patients hundreds or thousands of miles away, bringing specialized care to underserved areas. This democratizes access to high-quality healthcare, transcending geographical barriers.
The future of healthcare robotics hinges on continued research and development, supportive regulatory frameworks, and a commitment from healthcare leaders to embrace innovation. While challenges will persist, the trajectory points towards a future where robots are indispensable partners in delivering equitable, efficient, and exceptionally high-quality healthcare to all US citizens.
Key Strategies for Successful Robotics Adoption
Adopting robotics in US hospitals is not merely about purchasing new equipment; it’s a strategic undertaking that requires careful planning, dedicated resources, and a holistic approach. For successful integration, hospitals must consider various facets, from initial assessment and staff engagement to meticulous implementation and continuous optimization. Without a clear roadmap, even the most advanced technology might fail to deliver its promised benefits.
A crucial first step is a comprehensive needs assessment. Hospitals should identify specific pain points, bottlenecks, or areas where current processes are inefficient or prone to errors. This assessment will help determine which robotic solutions are most relevant and will provide the greatest impact. It’s not about adopting technology for technology’s sake, but rather about addressing tangible challenges with innovative solutions.
Building a Robust Implementation Framework
Once needs are identified, developing a multi-disciplinary implementation team is vital. This team should include representatives from clinical staff, IT, operations, finance, and legal departments. Their collective expertise will ensure that all critical aspects—from technical integration to ethical considerations and financial viability—are thoroughly addressed. This collaborative approach fosters buy-in and streamlines the decision-making process.
- Pilot Programs: Start small with controlled trials to validate effectiveness and identify kinks.
- Phased Rollout: Implement systems gradually to minimize disruption and allow for adjustments.
- Dedicated Leadership: Appoint project managers with clear authority and responsibility.
Training and education are arguably the most critical components of successful adoption. Staff members, from surgeons to nurses and technicians, must be thoroughly trained on how to operate, maintain, and interact with the new robotic systems. This training should be ongoing, addressing new features, troubleshooting, and best practices. Investing in staff proficiency ensures maximum utilization of the technology and builds confidence.
Furthermore, establishing robust performance metrics is essential. Hospitals need to track key indicators such as efficiency gains, error reduction rates, patient satisfaction scores, and ROI to evaluate the success of their robotic investments. Regular monitoring allows for prompt adjustments and ensures that the technology consistently aligns with organizational goals.
Finally, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement is paramount. Healthcare is an ever-evolving field, and robotic technology is advancing rapidly. Hospitals must be prepared to learn from their experiences, adapt to new advancements, and continually seek ways to optimize their robotic infrastructure. This forward-thinking approach ensures long-term sustainability and competitiveness in the dynamic healthcare landscape.
The Societal Impact: Beyond the Hospital Walls
The investment in healthcare robotics extends far beyond the immediate confines of hospital walls, impacting society in profound ways. As these technologies become more integrated, their influence will ripple through patient communities, medical education, public perception of healthcare, and even the broader economy. Understanding this wider societal impact is crucial for a holistic view of robotic transformation.
One direct societal benefit is improved public health. By reducing medical errors and increasing the efficiency of care delivery, robotics contributes to healthier communities. Fewer adverse events mean fewer instances of prolonged illness, disability, or premature death attributed to healthcare-related issues. This elevates the overall quality of life for citizens, fostering greater trust in the healthcare system.
Shaping Healthcare Workforce and Accessibility
While often a point of concern, the integration of robotics will not necessarily lead to widespread job displacement but rather a transformation of the healthcare workforce. Routine and repetitive tasks will be automated, freeing up human professionals to focus on complex decision-making, patient empathy, and innovative research. This shift necessitates new skill sets and opportunities for specialized training in robotics operation, maintenance, and data analysis.
- Evolution of Roles: Shift from manual tasks to oversight and complex care.
- New Job Creation: Demand for robotics engineers, technicians, and data analysts.
- Enhanced Training: Need for ongoing education in robotic technologies for clinical staff.
Robotics also holds the potential to significantly enhance healthcare accessibility, particularly in underserved rural areas. Through advanced telemedicine and remote-controlled robotic systems, specialized procedures and consultations can be delivered without requiring patients to travel long distances. This equitable distribution of high-quality care can help bridge existing healthcare disparities.
Furthermore, the increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness brought about by robotics can contribute to a more sustainable healthcare system. Reduced operational costs and error rates can alleviate some of the financial pressures on hospitals, potentially leading to more affordable care for patients in the long run. This, in turn, can contribute to overall economic productivity by maintaining a healthier workforce.
Beyond these tangible benefits, the societal perception of healthcare will evolve. A system perceived as cutting-edge, efficient, and highly precise will likely foster greater public confidence and encourage proactive health engagement. The narrative shifts from a reactive model to one characterized by proactive, technologically supported wellness. The journey of healthcare robotics is thus a shared one, shaping not just how care is delivered, but also how society views and experiences health.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🚀 Boosted Efficiency | Robots automate tasks, streamline workflows, and optimize resource allocation in hospitals. |
| 🛡️ Error Reduction | Precision robotics in surgery and pharmacy drastically cuts down human errors. |
| 💰 Investment ROI | Long-term savings from efficiency and error reduction often outweigh high upfront costs. |
| 💡 Future Outlook | AI-powered micro-robots and remote care represent the next wave of innovation. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Healthcare Robotics
▼
The main benefits include significant improvements in operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, substantial reduction in medical errors through enhanced precision and consistency, and ultimately, better patient outcomes. Robots handle physically demanding or monotonous jobs, freeing human staff to focus on complex patient care and critical decision-making.
▼
Surgical robots, like the da Vinci system, offer surgeons enhanced dexterity, magnified 3D vision, and tremor filtration. These capabilities allow for more precise, minimally invasive procedures. This often leads to smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, decreased risk of infection, and faster patient recovery, all contributing to a lower incidence of errors and complications.
▼
The ROI timeframe for healthcare robotics can vary widely depending on the specific technology, hospital size, and implementation strategy. While initial costs are high, hospitals often see returns within 3-7 years due to savings from increased efficiency, reduced errors, lower liability costs, and improved patient satisfaction leading to higher patient volumes and favorable reimbursements.
▼
Yes, significant challenges include ensuring compatibility with current IT infrastructure and electronic health records (EHRs), managing workflow disruptions during implementation, and overcoming potential staff resistance. Comprehensive planning, robust IT upgrades, thorough staff training, and clear communication are crucial to navigate these integration hurdles successfully.
▼
Robotics is expected to transform, rather than simply displace, the healthcare workforce. While some routine tasks will be automated, new roles will emerge in robotics operation, maintenance, and data analysis. Clinical staff will pivot towards more complex patient care, empathetic interactions, and specialized procedures, emphasizing the need for continuous skill development and adaptation.
Conclusion
The strategic incorporation of robotics into US hospitals stands as a transformative pillar for modern healthcare. As evidenced, the tangible benefits span from dramatically improved operational efficiencies and substantial reductions in medical errors to enhanced patient safety and overall clinical outcomes. While the investment landscape presents its complexities, the long-term ROI derived from streamlined workflows, optimized resource allocation, and a higher standard of care positions robotics not just as an innovative tool, but as an indispensable component for the future sustainability and excellence of the American healthcare system. Embracing this technological evolution requires foresight, commitment, and a collaborative spirit, ultimately paving the way for a more robust, reliable, and patient-centric healthcare experience across the nation.





